38 draw and label a segment of dna showing its helix and complementary base pairing.
bio anthro quiz 3 Flashcards | Quizlet Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and complementary base pairing. Verified answer. BIOLOGY. Write a brief proposal for why GPS technology and surveying should be used to study changes on a low-lying part of the coast. Verified answer. BIOLOGY. bio pt 5 Flashcards | Quizlet Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and complementary base pairing. ... - Three main stages: unwinding, base pairing, joining. unwinding. DNA helicase (enzyme) unzips a molecule of DNA ... long strands of RNA nucleotides that are formed from a complementary strand of DNA - travel from the nucleus to the ribosome for protein ...
DOC Chapter 12: RNA, DNA, and Protein Synthesis - COACH ANDERSON'S BLOG 1. Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and complementary base pairing. 2. Indicate the sequence of the template strand of DNA if the non-template strand has the sequence: ATGGGGCGC 3. Describe the role of DNA helicase and DNA polymerase. 4. Summarize the process by which the DNA code is made into a protein. 5.
Draw and label a segment of dna showing its helix and complementary base pairing.
Double Helix - Genome.gov The discovery of DNA's double-helical structure in the 1950s was perhaps the most significant biological accomplishment of the 20th century. Knowledge of this remarkably clever structure, involving two complementary strands of DNA that each provide the template for making the other strand, provided a key insight about how it was that DNA could serve as the information molecule of all living ... Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and ... Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and complementary base pairing. Describe the structure of eukaryotic chromosomes. ... All tutors are evaluated ... What Is the Complementary Base Pairing Rule? - Sciencing Two complementary strands of DNA come together thanks to hydrogen bonding between the nitrogenous bases that allows DNA to make a ladder-like form that twists into the famous double-helix. It's bonding between the nitrogenous bases that allows for this structure to form.
Draw and label a segment of dna showing its helix and complementary base pairing.. Answered: Draw a segment of DNA, labeling all… | bartleby Draw a segment of DNA, labeling all important chemical groups within the molecule. Describe the chemical and physical structure of DNA in words. Draw a nucleotide and clearly laber its three component parts. Compare the base pair of DNA to the base pair of RNA? Hydrogen Bonding in DNA Base Pairs" - CBM DNA Double Helix. One key point to notice in the DNA double helix structure is that the planar nitrogenous bases from the two strands are pointing toward each other, in the middle of the helix. Pairs of nitrogenous bases are set in the same plane, and interact with each other via hydrogen bonding. These pairs are often referred to as base pairs ... Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram - Science Trends The structure of DNA and RNA is also different. DNA is known for its double helix structure. The double helix is two strands that are intertwined with one another thanks to the complementary bases. RNA is a single-stranded molecule by contrast. The double helix form of DNA helps keep the genetic code intact. chapter 12 section 1 - Assessment Page 332 Mylena Riera... a. It needs to replicate itself. Thus it's a double strand, and the "new" strands form on each of the old strands to form a new double helix. The base pairings ensures that the new strand will be the exact counterpart to the old strand. b. It needs to be able to store a lot of information it its molecule. It does this with only 4 bases.
DNA Replication (With Diagram) | Molecular Biology Primer is a small strand segment which is complementary to the template. It has a free 3′-OH end to which a new nucleotide can be added. In this way part of the new strand is already in place. Primer is hydrogen bonded to the template to form primer: template junction. Primer is short nucleotide strand (oligonucleotide). Chaper11Lesson1 - 11 Molecular Genetics ESSENTIAL ... - Course Hero Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and complementary base pairing. 5. Describe two characteristics that DNA needs to fulfill its role as a genetic material. Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and comple - Quizlet BIOLOGY Make a sketch of the double helix of DNA. Show how it unzips for replication and how complementary strands are built. Label the nitrogenous bases, replication fork, DNA polymerase, the original strand, and the new strand. CHEMISTRY A segment of a DNA strand has the base sequence ACGTTGGCT. a. PDF DNA Review Packet Key to Study - Allegany-Limestone High School other strand, the strands are said to be complementary. DNA copies itself through the process of replication: The two strands of the double helix unzip, forming replication forks. New bases are added, following the rules of base pairing (A with T and G with C). Each new DNA molecule has one original strand and one new strand.
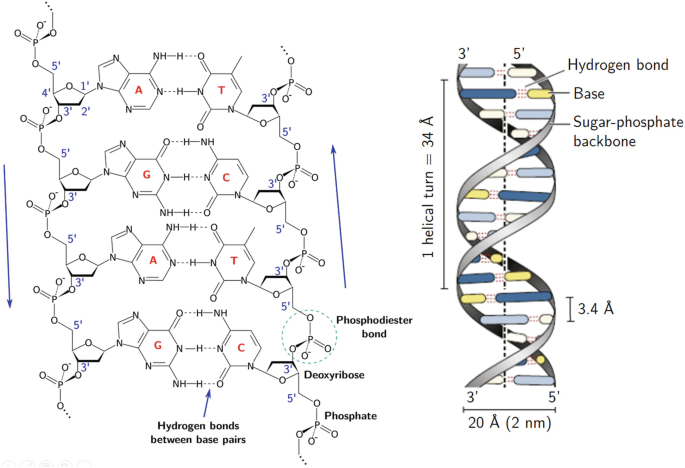
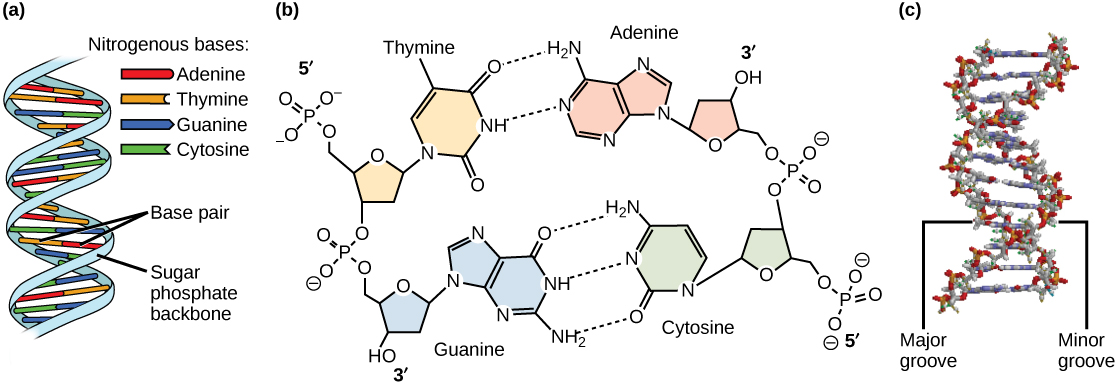
The Structure and Function of DNA - Molecular Biology of the Cell ... A DNA Molecule Consists of Two Complementary Chains of Nucleotides. A DNA molecule consists of two long polynucleotide chains composed of four types of nucleotide subunits. Each of these chains is known as a DNA chain, or a DNA strand.Hydrogen bonds between the base portions of the nucleotides hold the two chains together ().As we saw in Chapter 2 (Panel 2-6, pp. 120-121), nucleotides are ... Discovery of the structure of DNA (article) | Khan Academy Base pairing. In Watson and Crick's model, the two strands of the DNA double helix are held together by hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases on opposite ... Base pairing - Structure of DNA - Higher Biology Revision - BBC The nucleotides are identical except for the base, which can be an adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine. There are chemical cross-links between the two strands in DNA, formed by pairs of bases... DNA function & structure (with diagram) (article) - Khan Academy Chromosomes are very long structures consisting of two DNA polymers, joined together by hydrogen bonds connecting complementary base pairs. A chromosome is divided into segments of double-stranded DNA called genes. Each gene is further divided into three nucleotide subsegments called codons
Complementary Base Pairing: Definition & Explanation - Study.com Learn about the structure and composition of the DNA molecule, the Chargaff Rule on the structure of DNA, and how complementary base pairing occurs. Updated: 08/25/2021 Create an account
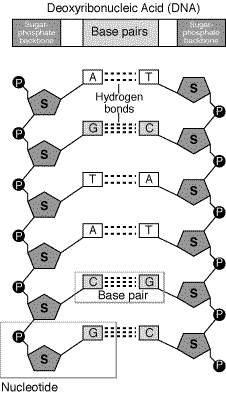
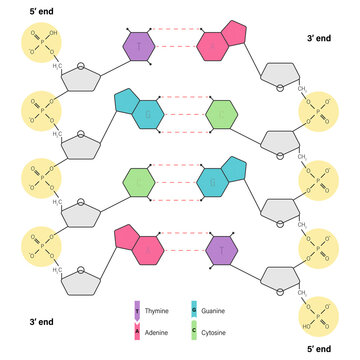
DNA: Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine & Complementary Base Pairing C will only bond with G and A will only bond with T in DNA. Because of complementary base pairing, the hydrogen-bonded nitrogenous bases are often referred to as base pairs. DNA Strands are ...
Biology U4 Q3 Flashcards | Quizlet Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and complementary base pairing. Verified answer. BIOLOGY. Explain why water dissolves so many different substances. Verified answer. BIOLOGY. Why are the light and chlorophyll needed for photosynthesis? Verified answer. Subjects. Arts and Humanities. Languages. Math. Science.
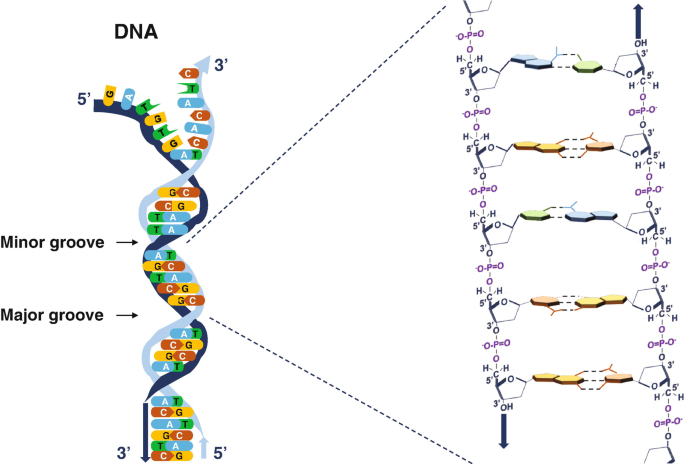
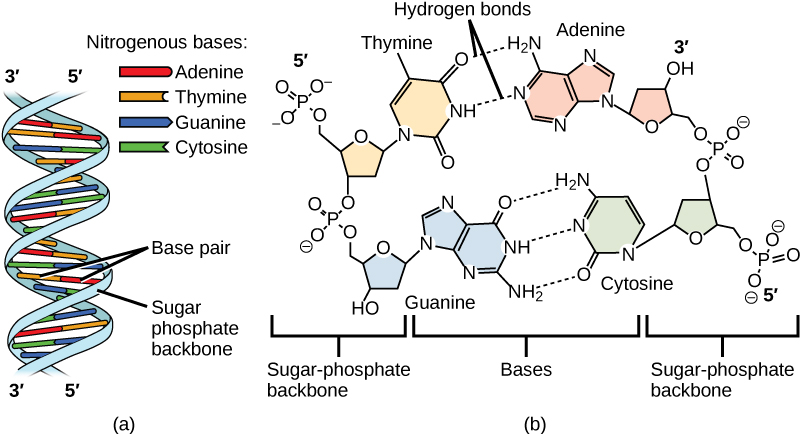
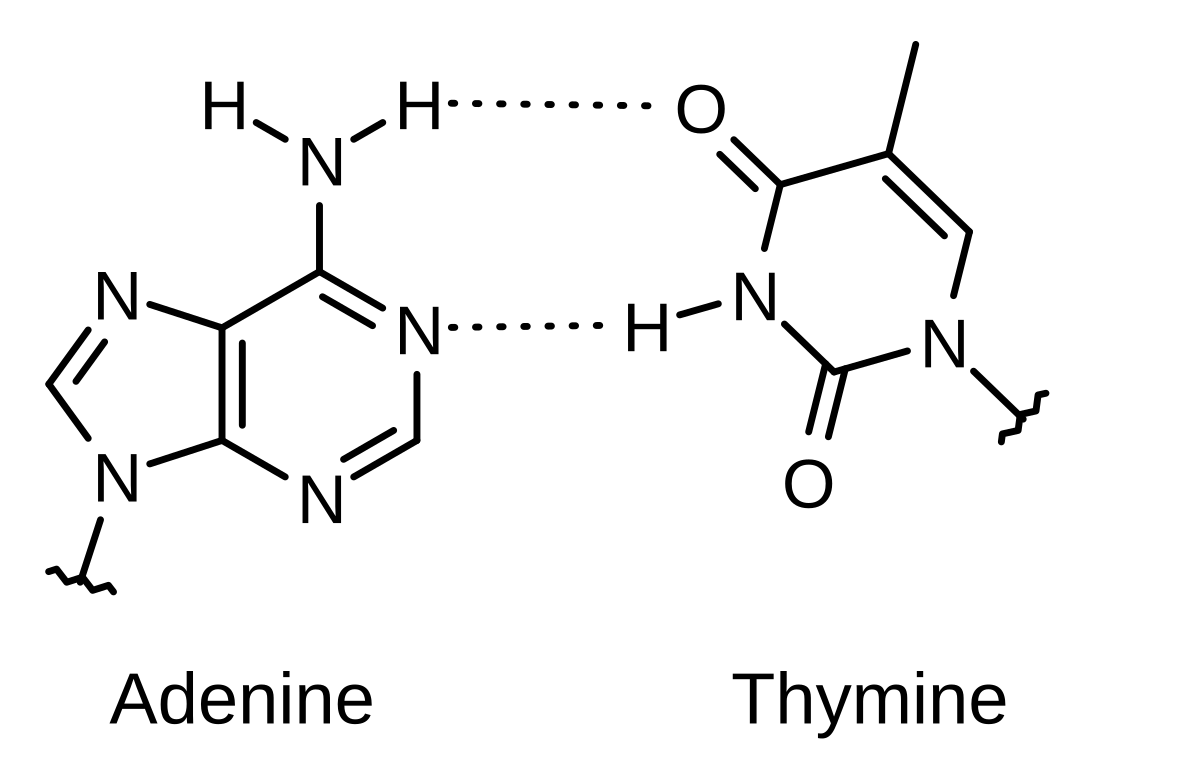
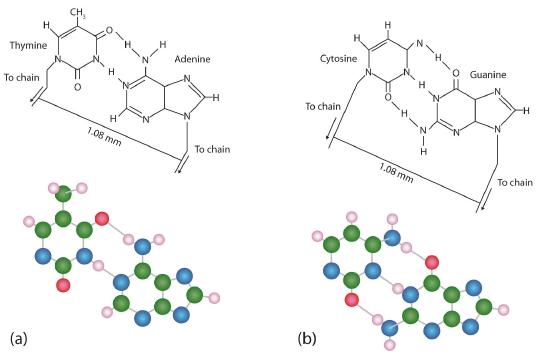
Draw and label a segment of dna showing its helix and complementary ... The first image is a diagram that illustrates the base paring of DNA. First, there is the ribose-phosphate backbone that keeps the DNA together. Then the bases thymine and adenine are joined together by two hydrogen bonds. On the other hand, the bases guanine and cytosine are joined together by three hydrogen bonds.
BIOLOGY101- chapter 6 Flashcards - Quizlet It is one of the four building nucleotides required for DNA synthesis. ... RNA molecules are produced by copying part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA into a complementary sequence in RNA. Verified answer. BIOLOGY. The freezing point of water is a (physical/chemical) property. ... Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and ...
The 4 DNA Bases and Their Strict Pairing Rules - Biology Wise The DNA of all the living beings is composed of just four bases i.e. Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G), and Cytosine (C). The various juxtapositions of these 4 bases give rise to the genetic codes of all the biota on the planet. Know more about these DNA bases in this post. Home / Uncategorized / The 4 DNA Bases and Their Strict Pairing Rules.
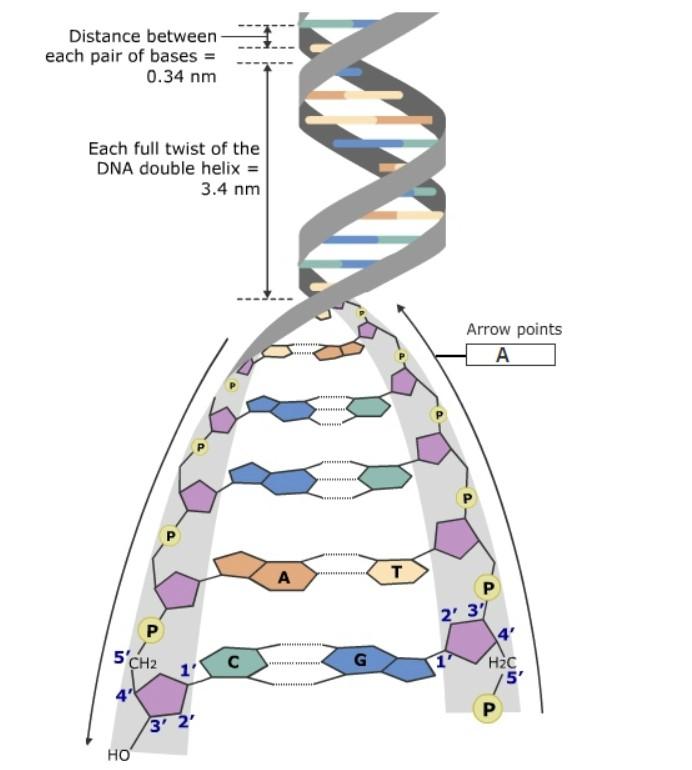
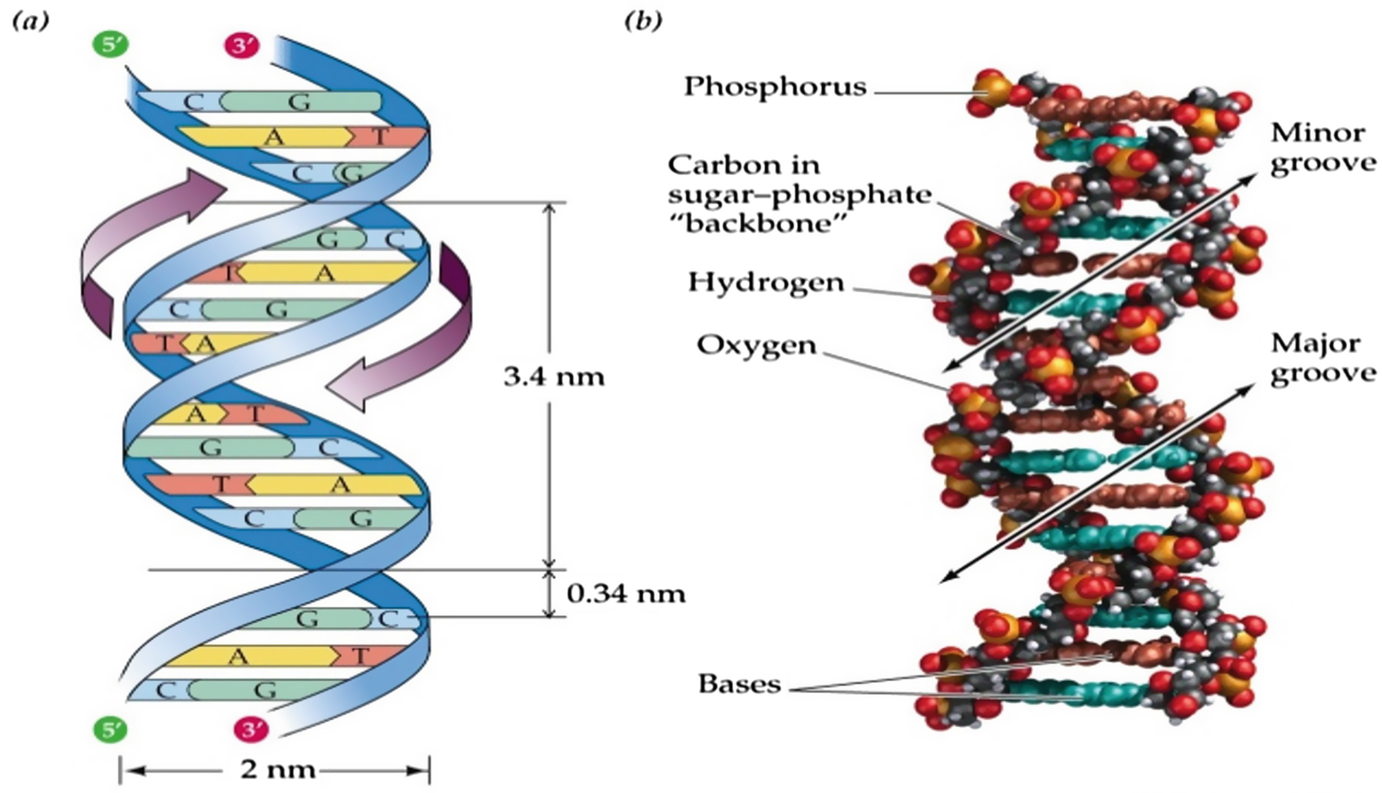
DNA Structure - Visible Body DNA is a macromolecule consisting of two strands that twist around a common axis in a shape called a double helix. The double helix looks like a twisted ladder—the rungs of the ladder are composed of pairs of nitrogenous bases ( base pairs ), and the sides of the ladder are made up of alternating sugar molecules and phosphate groups.
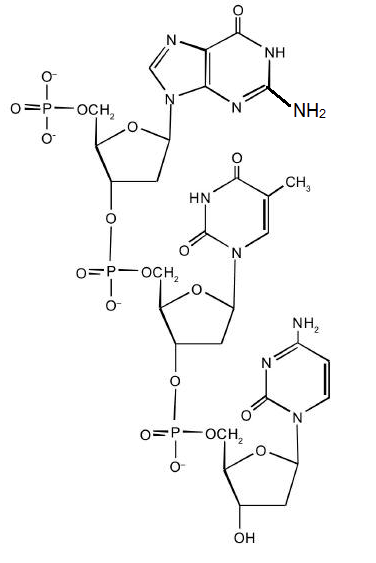
9.1 The Structure of DNA - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition The DNA molecule is a polymer of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), and a phosphate group. There are four nitrogenous bases in DNA, two purines (adenine and guanine) and two pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). A DNA molecule is composed of two strands.
Base Pair - Genome.gov A base pair consists of two complementary DNA nucleotide bases that pair together to form a "rung of the DNA ladder." DNA is made of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder — a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups.
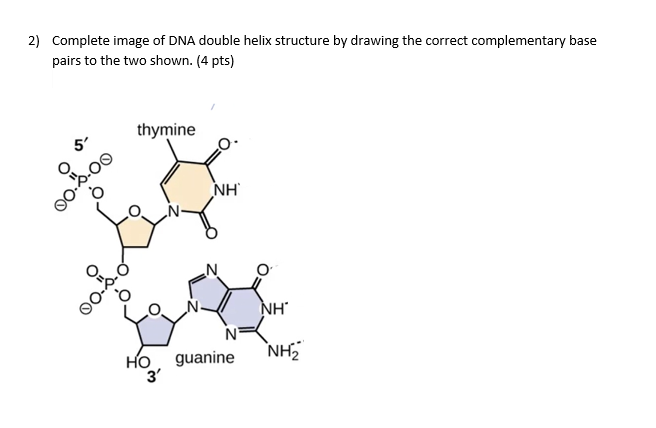
Answered: Draw the following segment of DNA… | bartleby Q: Draw the following strands of DNA 5' C-A-T 3' as well as the complementary base pairing strand… A: Two strands of DNA twist around one another to form a double helix DNA and both are in anti-parallel…
The Structure of DNA Knowing the base pairing convention of A always pairing with T and G always pairing with C makes the complementary strand of the molecule understood. It is this feature of complementary base pairing that insures an exact duplicate of each DNA molecule will be passed to its daughter cells when a cell divides.
What Is the Complementary Base Pairing Rule? - Sciencing Two complementary strands of DNA come together thanks to hydrogen bonding between the nitrogenous bases that allows DNA to make a ladder-like form that twists into the famous double-helix. It's bonding between the nitrogenous bases that allows for this structure to form.
Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and ... Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and complementary base pairing. Describe the structure of eukaryotic chromosomes. ... All tutors are evaluated ...
Double Helix - Genome.gov The discovery of DNA's double-helical structure in the 1950s was perhaps the most significant biological accomplishment of the 20th century. Knowledge of this remarkably clever structure, involving two complementary strands of DNA that each provide the template for making the other strand, provided a key insight about how it was that DNA could serve as the information molecule of all living ...


















Post a Comment for "38 draw and label a segment of dna showing its helix and complementary base pairing."